Most people know ovulation as the time in a woman’s menstrual cycle when she is most likely to conceive. But ovulation is much more than that. It is a process that occurs in both men and women, and it has important implications for fertility. In this blog post, we will discuss ovulation in detail – what it is, how it works, and why it matters. We’ll also answer some common questions about ovulation, such as “when does ovulation occur?” and “how can I tell if I’m ovulating?” So if you’re curious about ovulation, read on!
Table of Contents
What is ovulation?
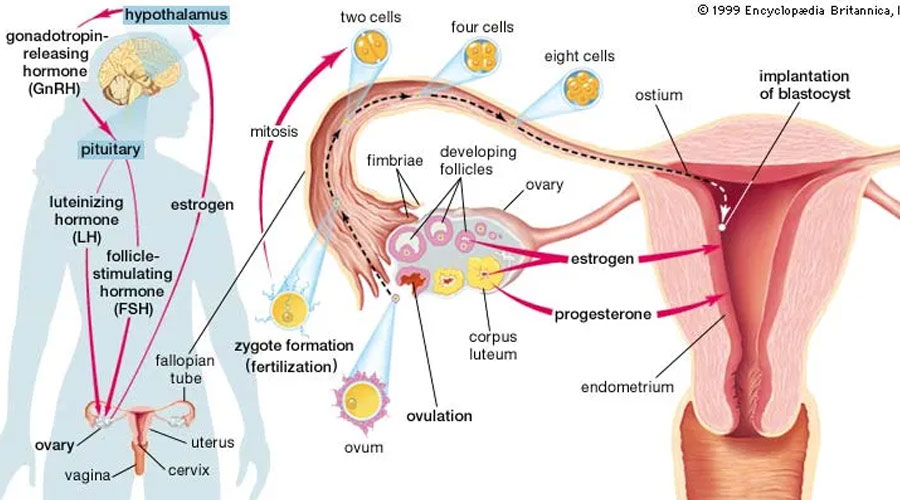
In short, ovulation is the release of an egg from one of the ovaries. This process happens in both men and women, but it is much more important for fertility in women. In fact, ovulation is the most critical step in the conception of the female reproductive system. Your hypothalamus (which is in charge of maintaining your hormone levels) sends out a message to your pituitary gland which then sends out the follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). This FSH triggers a few of your follicles to develop into mature eggs. One of these will develop into the dominant follicle, which will release a mature egg and the others will disintegrate.
Ovulation occurs when a hormone called LH (luteinizing hormone) surges. This surge triggers the ovary to release an egg. The egg then travels down the fallopian tube to the uterus, where it may be fertilized by sperm if intercourse takes place around that time.
Ovulation is essential for conception because it’s the only time when you can actually get pregnant. Sperm can live inside a woman’s body for up to five days, so if intercourse occurs near the time of ovulation, there is a good chance that sperm will be around to fertilize the egg.
How to track your ovulation cycle?
Most women ovulate around 14 days before their next menstrual period. However, this can vary from woman to woman, and even from month to month. If you’re trying to get pregnant, it’s important to track your ovulation cycle so that you know when you’re most likely to ovulate.
There are a few different ways to do this:
- tracking basal body temperature
- using ovulation predictor kits
- charting your cervical mucus

If you’re trying to get pregnant, it’s important to know when ovulation occurs. There are several ways to track ovulation:
- Tracking your basal body temperature (BBT) can help you determine when ovulation has occurred. Your BBT is the temperature of your body at rest. You can take your BBT with a Basal Body Temperature Thermometer each morning before getting out of bed. After ovulation, your BBT will rise slightly and stay elevated until the start of your next period.
- Ovarian monitoring using an over-the-counter ovulatory predictor kit (OPK) can also help you determine when ovulation is about to occur. OPKs work by detecting the presence of the luteinizing hormone (LH) in your urine. LH is a hormone that increases just before ovulation.
- Another way to track ovulation is to keep a record of changes in your cervical mucus. Just before ovulation, you may notice an increase in clear, slippery mucus. This is called fertile-quality cervical mucus and it’s a good sign that ovulation is about to occur.
If you’re trying to get pregnant, tracking ovulation can help you determine when you’re most likely to conceive. There are several different ways to track ovulation, so talk to your doctor about which method would be best.
Each of these methods has its own advantages and disadvantages, so you may want to try out several until you find one that works best for you.
When does ovulation occur?
As we mentioned earlier, ovulation typically occurs around 14 days before the next period. However, it can vary from woman to woman and month to month. So if you’re trying to get pregnant, it’s important to track your ovulation cycle so that you know when you’re most likely to ovulate.
It is possible for some women to ovulate more than once a month, but this is not common. Most women only ovulate once per month.

The symptoms of ovulation vary from woman to woman. However, many women experience changes in their cervical mucus and basal body temperature during ovulation. You may also notice an increase in sex drive or a change in your cervical position.
If you’re trying to get pregnant, it’s important to pay attention to your body and look for any changes that may be associated with ovulation.
Fertility vs. ovulation
It’s important to understand the difference between fertility and ovulation. Many people think that ovulation is the only time when you can get pregnant, but this is not true.
Fertility is the ability to conceive a child. Ovulation is just one part of fertility. There are many other factors that contribute to fertility, such as the health of the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and uterus; the presence of sperm; and timing (intercourse must take place around the time of ovulation). It is important to have fertility awareness-based methods.
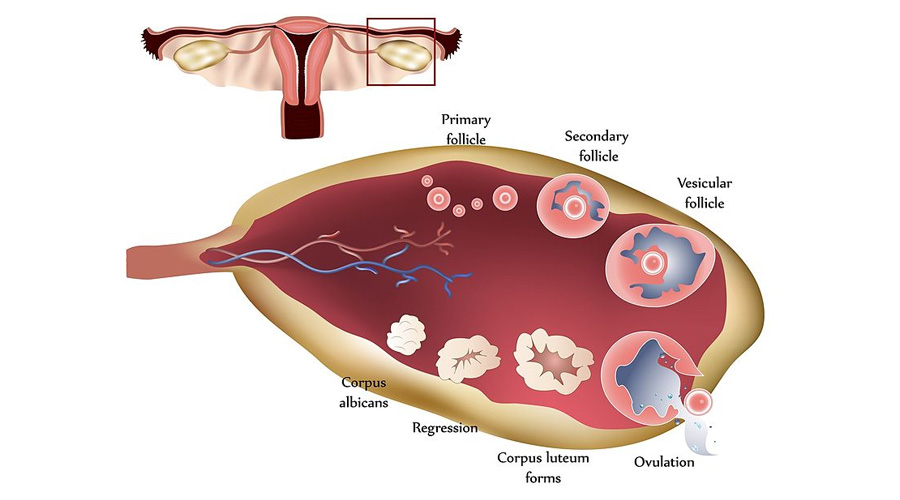
Ovulation is an important part of fertility, but it is not the only factor that matters. If you’re trying to get pregnant, it’s important to talk to your doctor about all of the factors that may affect your fertility. It’s common to have irregular ovulation just after pregnancy and breastfeeding, and during the years approaching menopause.
Phases of the menstrual cycle
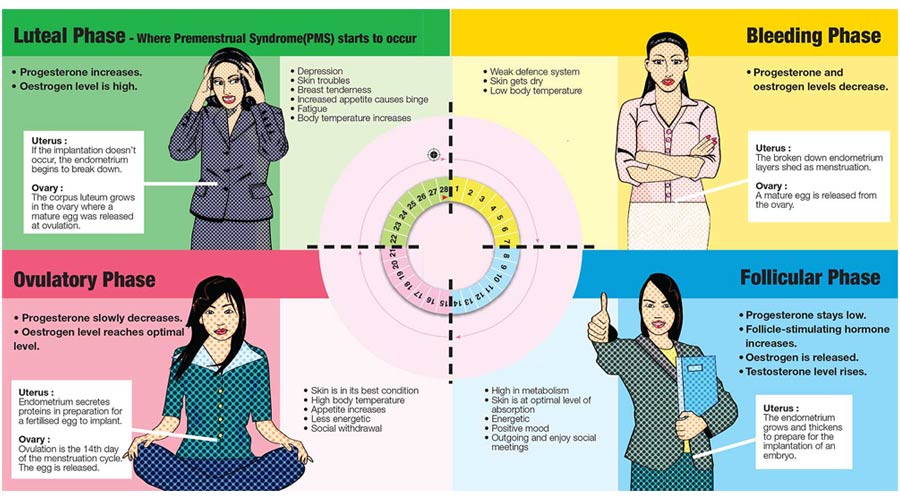
The human menstrual cycle is divided into three phases: the follicular phase, ovulatory phase, and luteal phase.
- The follicular phase begins on the first day of your period and ends when ovulation occurs. This is the time when the ovaries are preparing to ovulate.
- The ovulatory phase begins with ovulation and lasts until the start of menstruation. This is the time when the egg is released from the ovary.
- The luteal phase begins after ovulation and ends when you get your period. This is the time when the fertilized egg travels down the fallopian tube to the uterus. If fertilized by sperm, it will implant in the uterine wall and begin to grow into a baby. If not, the uterine lining of the uterus will fall down and will be monthly menstrual cycles.
These phases can vary from woman to woman and month to month. If you’re trying to get pregnant and have sexual intercourse, it’s important to be aware of the different stages of the menstrual cycle so that you know when ovulation is most likely to occur. Irregular menstrual cycles also are common so make sure to pay your doctor a visit.
The ovulation cycle divided into two parts
The ovulation cycle is divided into two parts: the follicular phase and the luteal phase. The follicular phase begins on the first day of your period and ends when ovulation occurs. This is the time when the ovaries are preparing to ovulate.
The luteal phase begins after ovulation and ends when you get your period. This is the time when the egg travels down the fallopian tube to the uterus. If fertilized by sperm, it will implant in the uterine wall and begin to grow into a baby.
These phases can vary from woman to woman and month to month. If you’re trying to get pregnant, it’s important to be aware of the different stages of the menstrual cycle so that you know when ovulation is most likely to occur.
Health conditions that affect ovulation
There are many health conditions that can affect ovulation. Some of the most common include:
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a condition in which the ovaries produce too many hormones. This can lead to problems with ovulation.
- Thyroid disorders can also interfere with ovulation. An overactive or underactive thyroid can disrupt the normal functioning of the ovaries and affect ovulation.
- Diabetes mellitus is a condition in which the body does not produce enough insulin or cannot use insulin properly. This can also interfere with ovulation.
If you think you may have a health condition that affects ovulation, it’s important to see your doctor for diagnosis and treatment. Treatment for these conditions may help you ovulate more regularly and improve your chances of getting pregnant.
Excess prolactin
Prolactin is a hormone that helps with milk production during breastfeeding. However, too much prolactin can interfere with ovulation. If you’re not breastfeeding and you have high levels of prolactin, it can be a sign of a pituitary tumor.
This is a rare condition, but it’s important to see your doctor if you think you may have it. Treatment for a pituitary tumor may help improve ovulation.
Polycystic ovary syndrome
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a condition in which the ovaries produce too many hormones. This can lead to problems with ovulation. PCOS is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
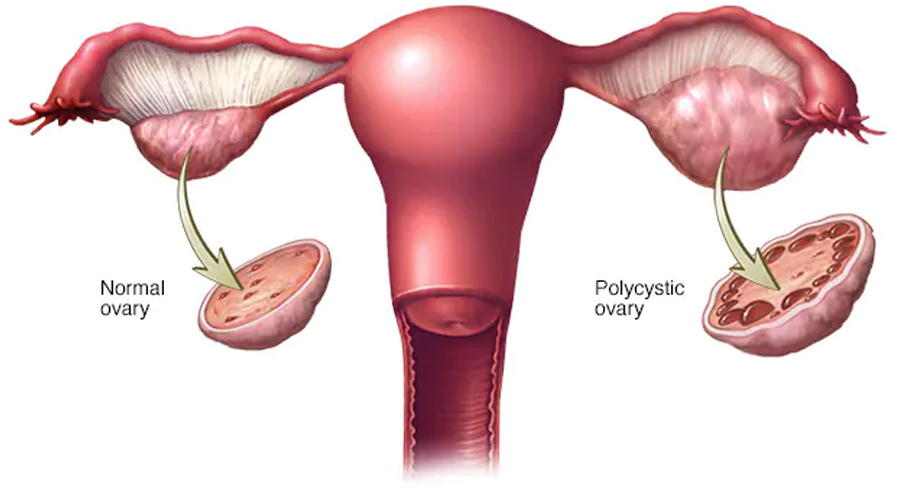
If you have PCOS, you may be at increased risk for other health conditions, such as type II diabetes and heart disease. Treatment for PCOS may include lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, or medication.
Inducing ovulation
If you’re having difficulty ovulating, your doctor may recommend ovulation induction. This is a procedure in which medications or injections are used to help the ovaries produce eggs. Ovulation induction can be done using clomiphene citrate (Clomid), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), human menopausal gonadotropin (hMG), and/or luteinizing hormone (LH). These medications work by stimulating the ovaries to produce eggs.
Premature ovarian insufficiency
Premature ovarian insufficiency (POI) is a condition in which the ovaries stop working before age 40. This can lead to problems with ovulation and infertility. POI is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. There is no cure for POI, but there are treatments that can help improve ovulation.
Hypothalamic dysfunction
The hypothalamus is a part of the brain that helps regulate ovulation. Hypothalamic dysfunction can lead to problems with ovulation. Treatment for this condition may include lifestyle changes, such as diet and exercise, or medication.
If you’re having difficulty ovulating, it’s important to see your doctor. There are several conditions that can cause ovulation problems, but there are also treatments that can help improve ovulation. Talk to your doctor about what treatment options are available to you.
Inference
Ovulation is the process of the ovary releasing an egg into the fallopian tube. It typically occurs about midway through the menstrual cycle, around day 14 (give or take a few days). The egg travels down the fallopian tube to the uterus where it may be fertilized by sperm. If fertilized, the egg will implant in the uterine wall and begin to grow into a baby.
There are many health conditions that can affect ovulation. Some of the most common include polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), thyroid disorders, diabetes mellitus, and excess prolactin. If you think you may have a health condition that affects ovulation, it’s important to see your doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
Treatment for these conditions may help you ovulate more regularly and improve your chances of getting pregnant. If you’re trying to get pregnant, tracking ovulation can help you determine when you’re most likely to conceive. There are several different ways to track ovulation, so talk to your doctor about which method would be best for you.
FAQ
Does ovulation mean pregnant?
No, ovulation is not a sign of pregnancy. Ovulation occurs when the ovary releases an egg into the fallopian tube. If fertilized by sperm, the egg may implant in the uterine wall and begin to grow into a baby. However, ovulation does not mean that you are pregnant.
How do I know I'm ovulating?
There are several different ways to track ovulation. Some women use ovulation predictor kits, which measure levels of luteinizing hormone (LH) in the urine. LH is a hormone that surges just before ovulation. Other women track their basal body temperature or cervical mucus changes to look for patterns that occur just before ovulation.
Still, others use a combination of these methods. Talk to your doctor about which method would be best for you.
What is a simple definition of ovulation?
The simple definition of ovulation is the process of the ovary releasing an egg into the fallopian tube. This typically occurs around day 14 (give or take a few days) of the menstrual cycle. Ovulation is necessary for pregnancy to occur, as it is when the egg may be fertilized by sperm. If fertilized, the egg will implant in the uterine wall and begin to grow into a baby.
There are many health conditions that can affect ovulation, so it’s important to see your doctor if you’re having trouble ovulating.
What happens during ovulation?
The ovary releases an egg into the fallopian tube. The egg travels down the fallopian tube to the uterus where it may be fertilized by sperm. If fertilized, the egg will implant in the uterine wall and begin to grow into a baby. There are many things that can affect ovulation, so it’s important to see your doctor if you’re having trouble ovulating.
What are the stages of ovulation?
The ovulation process typically takes about 24 hours and can be divided into four stages:
- The follicular phase: This is the first stage of ovulation when the ovary is preparing to release an egg.
- The ovulatory phase: This is the second stage of ovulation when the ovary releases an egg into the fallopian tube.
- The luteal phase: This is the third stage of ovulation when the egg travels down the fallopian tube to the uterus. If fertilized, it will implant in the uterine wall and begin to grow into a baby.
- The menstrual phase: This is the fourth and final stage of ovulation when bleeding occurs if pregnancy has not occurred. It marks the beginning of the next menstrual cycle.
